Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murakami, Kenta*; Arai, Taku*; Yamada, Koji*; Momma, Kensuke*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Nakagawa, Nobuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2024/03
This paper studied the future vision of codes and standards in Japan by systematically comparing Japanese regulatory rules, standards, and industry guides related to long term operation with international safety standards, and confirmed that the Japanese standard system generally meets their recommendations. The recommendation for the future improvements of Japanese codes and standards were summarized into five items.
Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Mihara, Takeshi; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 195, p.110144_1 - 110144_11, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Izumi*; Otani, Akihito*; Okuda, Yukihiko; Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Takito, Kiyotaka; Okuda, Takahiro; Shimazu, Ryuya*; Sakai, Michiya*; Shibutani, Tadahiro*; Shiratori, Masaki*
Dai-10-Kai Kozobutsu No Anzensei, Shinraisei Ni Kansuru Kokunai Shimpojiumu (JCOSSAR2023) Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.143 - 149, 2023/10
In 2019, the JSME Code Case for seismic design of nuclear power plant piping systems was published. The Code Case provides the strain-based fatigue criteria and detailed inelastic response analysis procedure as an alternative design rule to the current seismic design, which is based on the stress evaluation by elastic response analysis. In 2022, it was approved to revise the Code Case with improving the cycle counting method for fatigue evaluation to the Rain flow method. In addition, the discussion to incorporate the elastic-plastic behavior of support structures is now in progress for the next revision of the Code Case. This paper discusses the contents and background of the 2022 revision, the progress of the next revision, and future tasks.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Li, C.-Y.; Watanabe, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-063, 86 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. The samples to be analyzed in this study were collected from wild Japanese macaques exposed in the ex-evacuation zone after the accident of 1F.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2022-011, 37 Pages, 2022/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. Two major mechanisms are expected for fission products (FPs) transfer from liquid to vapor phase. One is non-volatiles FPs transfer in the form of mists to the vapor phase in the tank, the other is volatilization of such as Ruthenium. These FPs transferred to the vapor phase in the tank could be released with water and nitric-acid mixed steam and NO gas flow to the environment. NO
gas flow to the environment. NO is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (
is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (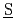 imulation of
imulation of 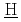 igh-level radio
igh-level radio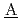 ctive
ctive 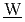 aste
aste 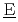 vaporation and
vaporation and 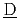 ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
Simanullang, I. L.*; Nakagawa, Naoki*; Ho, H. Q.; Nagasumi, Satoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Fujimoto, Nozomu*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 177, p.109314_1 - 109314_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Hideo; Bentaib, A.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Ruyer, P.*; Mascari, F.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Adorni, M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Topical Issues in Nuclear Installation Safety; Strengthening Safety of Evolutionary and Innovative Reactor Designs (TIC 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/10
Kato, Shinya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Akaev, A.*; Vurim, A.*; Baklanov, V.*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
The In-Vessel Retention (IVR) of molten-core in Core Disruptive Accidents (CDAs) is of prime importance in enhancing the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors. One of the main subjects in ensuring IVR is to design the Control Rod Guide Tube (CRGT) which allows effective discharge of molten core materials from the core region. The effectiveness of the CRGT design is assessed through CDA analyses, and it is reasonable for these analyses to develop a computer code collaborated with experimental researches. Thus, experiments addressing the discharge behavior of the molten-core materials through the CRGT have proceeded as one of the subjects in the collaboration research named the EAGLE-3 project, and the obtained experimental results are reflected in the development of the SIMMER code. In this project, a series of out-of-pile tests using molten-alumina as the fuel simulant was conducted to understand the discharge behavior of molten-core materials through the CRGT. In this study, in order to investigate the effect of an internal structure in the CRGT on the discharge behavior of the molten-core materials, the data of an out-of-pile test in which the molten-alumina penetrated to a duct with the internal structure were analyzed. In addition, the post-test analysis using the SIMMER code was conducted and the results were compared with the test results.
Li, C.-Y.; Watanabe, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Dai-26-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/07
Identifying accident scenarios that could lead to severe accidents and evaluating their frequency of occurrence are essential issues. This study aims to establish the methodology of the dynamic Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) for sodium-cooled fast reactors that can consider the time dependency and the interdependence of each event. Specifically, the Continuous Markov chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) method is newly applied to the SPECTRA code, which analyzes the severe accident conditions of nuclear reactors, to develop an evaluation methodology for typical external hazards. Currently, a fault-tree model of air coolers of decay heat removal system is implemented as the CMMC method, and a series of preliminary analysis of the plant's transient characteristics under the scenario of volcanic ashfall has been conducted.
Thwe Thwe, A.; Terada, Atsuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.573 - 579, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The simulations of the combustion of self-propagating hydrogen-air premixed flame are performed by an open-source CFD code. The flame propagation behavior, flame radius, temperature and pressure are analyzed by varying the initial laminar flame speed and grid size. When the initial laminar speed increases, the thermal expansion effects become strong which leads the increase of flame radius along with the increase of flame surface area, flame temperature and pressure. A new laminar flame speed model derived previously from the results of experiment is also introduced to the code and the obtained flame radii are compared with those from the experiments. The formation of cellular flame fronts is captured by simulation and the cell separation on the flame surface vividly appears when the gird resolution becomes sufficiently higher. The propagation behavior of cellular flame front and the flame radius obtained from the simulations have the reasonable agreement with the previous experiments.
Malins, A.; Lemoine, T.*
Journal of Open Source Software (Internet), 7(71), p.3318_1 - 3318_6, 2022/03
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-050, 82 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and of animal experiments.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-013, 20 Pages, 2022/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. An idea has been proposed to implement a steam condenser as an accident countermeasure. This measure is expected to prevent nitric acid steam diffusing in facility building and to increase gaseous Ru trapping ratio into condensed water. A simulation study has been carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building to analyze the efficiency of steam condenser. In this study, SCHERN computer code simulates chemical behaviors of Ru in nitrogen oxide, nitric acid and water mixed vapor based on the conditions obtained from simulation with thermal-hydraulic computer code MELCOR. The effectiveness of steam condenser has been analyzed quantitively in preventing mixed vapor diffusion and gaseous Ru trapping effect. Some issues to be solved in analytical model has been also clarified in this study.
Soba, A.*; Prudil, A.*; Zhang, J.*; Dethioux, A.*; Han, Z.*; Dostal, M.*; Matocha, V.*; Marelle, V.*; Lasnel-Payan, J.*; Kulacsy, K.*; et al.
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-005, 25 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation equation of Ru mass transfer coefficient across the vapor-liquid surface, which can be useful for quantitative simulation of Ru mitigating behavior, has been obtained from data analyses of small-scale experiments conducted to clarify gaseous Ru migrating behavior under steam-condensing condition. A simulation study has been also carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building successfully to demonstrate the feasibility of quantitative estimation of amount of Ru migrating in the facility using the obtained correlation equation implemented in SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitrogen oxide based on the condition also simulated thermal-hydraulic computer code.
Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Junichi*; Ito, Masahiro*; Ishitani, Ikuo*; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Otsuka, Satoshi
Nuclear Technology, 207(8), p.1280 - 1289, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)Computer codes for irradiation behavior analysis of a fuel pin and a fuel pin bundle and for coolant thermal hydraulics analysis were coupled into an integrated code system. In the system, each code provides data required by other codes and the analyzed results are shared among them. The system allows for the synthesizing of analyses of thermal, chemical and mechanical behaviors in a fuel subassembly under irradiation. A test analysis was made for a fuel subassembly containing a mixed oxide fuel pin bundle irradiated in a fast reactor. The results of the analysis were presented with transverse cross-sectional images of the fuel subassembly and three-dimensional images of a fuel pin and fuel pin bundle models. For detailed evaluation, various irradiation behaviors of all fuel pins in the subassembly were analyzed and correlated with irradiation conditions.
Udagawa, Yutaka; Tasaki, Yudai
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-007, 56 Pages, 2021/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has released FEMAXI-8 in 2019 as the latest version of the fuel performance code FEMAXI, which has been developed to analyze thermal and mechanical behaviors of a single fuel rod in mainly normal operation conditions and anticipated transient conditions. This report summarizes a newly developed model to analyze intragranular fission gas behaviors considering size distribution of gas bubbles and their dynamics. While the intragranular fission gas behavior models implemented in the previous FEMAXI versions have supported only treating single bubble size for a given fuel element, the new model supports multiple gas groups according to their size and treats their dynamic behaviors, making the code more versatile. The model was first implemented as a general module that takes arbitrary number of bubble groups and spatial mesh division for a given fuel grain system. An interface module to connect the model to FEMAXI-8 was then developed so that it works as a 2 bubble groups model, which is the minimum configuration of the multi-grouped model to be operated with FEMAXI-8 at the minimum calculation cost. FEMAXI-8 with the new intragranular model was subjected to a systematic validation calculation against 144 irradiation test cases and recommended values for model parameters were determined so that the code makes reasonable predictions in terms of fuel center temperature, fission gas release, etc. under steady-state and power ramp conditions.
Li, C.-Y.; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/07
The capability of stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed are the main issues for achieving IVR (In-Vessel Retention). In the actual situation, the debris bed is composed of mixed-density debris particles. Hence, when these mixed-density debris particles were launched to re-distribute, the debris bed would possibly form a density-stratified distribution. For the proper evaluation of this scenario, the multi-physics model of CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics is established to investigate the coolability and re-criticality on the heterogeneous density-stratified debris bed with considering the particle relocation. The CFD-DEM model has been verified by utilizing water injection experiments on the mixed-density particle bed in the first portion of this research. In the second portion, the coupled system of the CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics model is applied to reactor cases. Afterward, the debris particles' movement, debris particles' and coolant's temperature, and the k-eff eigenvalue are successfully tracked. Ultimately, the relocation and stratification effects on debris bed's coolability and re-criticality had been quantitatively confirmed.